Income Statement
The first of the 4 main financial statements is the income statement, also known as the “Profit and Loss statement”, “P&L statement”, “expense statement”, “statement of financial results”, and so on.
So what is it?
An income statement is a financial statement that states the losses incurred and profits accrued by a company over a period of time. This period could range from a fiscal quarter to a financial year.
More specifically, it reflects the revenues and expenses of a company over a particular time.
Income statements provide the data to predicate the revenue generating potential of a company, its operational efficiency, and identifying the profit making verticals as well as lossy investments.
It demonstrates the flow of revenue into a company and how the revenue is managed to generate net income or profit.
- Note: Every public company and every company registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) must compile their income statement and submit it to the SEC for public access.
How is the Income Statement Organized?
The primary revenue categories of information in the income statement include:
- Operating Revenue
The primary operations or activities of a business generate its operating revenue.
- Non-operating Revenue
This is revenue realized from secondary business activities, often different from the primary business of a company.
- Gains
Other incomes that a company generates are called “gains”. When a company’s assets, equipment or facility is sold, gains will be realized.
After the revenue section comes the expense section.
There are two major types of Expenses, these are expenses from primary activities and expenses from secondary activities.
- Expenses resulting from primary activities
These are the expenses that a company accrues during its primary business operations, like manufacturing of goods, wages paid for labor, sales expenses, maintenance expenses, utility fees and others.
- Expenses from secondary activities
These are expenses generated from activities that are not core to the business operations.
Losses
Losses occur when the expenses of a project or undertaking are greater than the revenue generated from those activities.
What is Net Income?
Below is the formula for calculating a company’s net income;
Net Income = (Revenue + Gains) – (Expenses + Losses)
Example of a Simple Income Statement
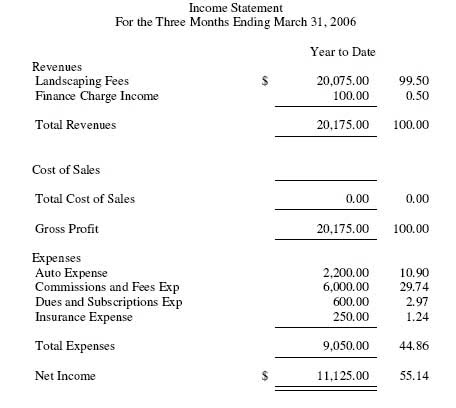
Uses of the Income Statement
The income statement has many uses. One of its many uses is to reflect the financial performance of a business to stakeholders. (For public companies, this includes public disclosure to external investors.)
The income statement of a business is also important to help the management make crucial decisions about the company.
Furthermore, an income statement helps to check the progress of a business in comparison to its peers in the industry.
